ISAs, or Individual Savings Accounts, have become a go-to choice for many people in the UK looking to save or invest their money smartly. The tax-advantages that come with these accounts make them quite popular. They also provide various solutions so that customers can save money in a way that suits their level of risk and financial objectives.
ISAs come in various forms, each with special advantages. These include Junior ISAs, Innovative Finance ISAs, Cash ISAs, Stocks and Shares ISAs, and Lifetime ISAs. These Individual Savings Accounts (ISAs) cater to various goals and objectives, including long-term or short-term savings, portfolio building, retirement planning, and providing cash for your child’s future.
Knowing how different ISAs differ is essential to helping people make informed financial decisions. This comprehensive guide will examine the specifics of each ISA, including its characteristics, eligibility conditions, and special benefits.
What Are ISAs?
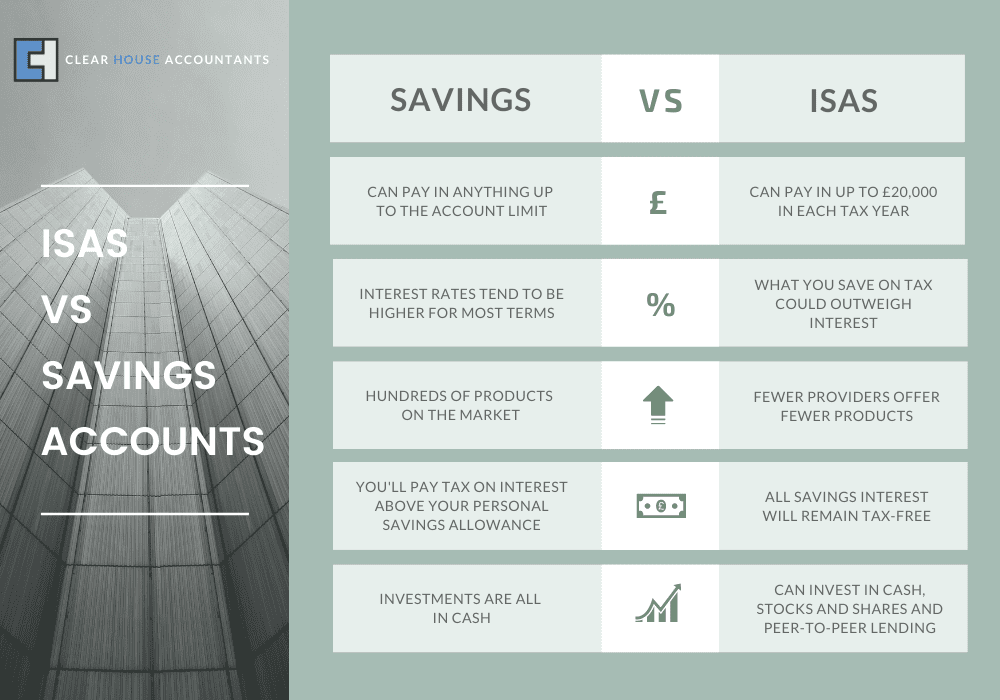
An Individual Savings Account, or ISA, is a tax-free savings account. It has a catch, though – there’s a limit to how much money you can stash or invest each tax year. This limit is often referred to as your annual Tax-free ISA allowance. Just so you know, for this tax year(24/25), your allowance is a sum of £20,000.
Think of an ISA like a safe box – everything you put inside is shielded from taxes. There are two types of ISAs to choose from: Cash ISAs and Stocks & and Shares ISAs.
When you have a regular savings account, your interest is considered income, so you must pay taxes. However, with an ISA, you enjoy an incredible perk – your interest is tax-free.
You can choose from a range of ISAs, and there’s no limit to how many you can have. Just remember that you can only pay into one of each type every tax year. You can’t go over the annual ISA allowance—which, for 2024/2025, is set at £20,000.
Benefits of an ISA
1- Your funds will experience tax-free growth
2- The maximum amount one can contribute within the current tax year 24/25 is at £20,000.
3- Your yearly allowance is reset each time a new tax year begins.
4- You can transfer your existing Individual Savings Accounts (ISAs) to your new ISA.
5- Children in the age range of 16 to 18 have the opportunity to possess both a Junior ISA and a regular Cash ISA.
6- Customised options exist to assist individuals in saving for their initial home purchase or retirement.
What is the ISA allowance?
For the tax year of 2024/25, you can contribute up to £20,000 to your ISA or a mix of ISAs. That’s the maximum amount you can put in over that tax year.
Keep in mind the tax year stretches from April 6th to April 5th of the following year. Also, just so you know, if you don’t use up all your full allowance in that tax year, any leftovers won’t roll over to the next.
Sure, you can have multiple ISAs at any given time, but in the same tax year, you can only contribute to one of each kind. For example, in 2024/2025, you could top up a Stocks and Shares ISA with a ‘With Profits’ option, a cash ISA, and a lifetime ISA. However, you can’t put money into two cash ISAs within the same tax year.
Some people prefer to distribute their allowance in this way. It enables them to potentially reap the benefits of an investment ISA while also keeping a portion of their savings in cash.
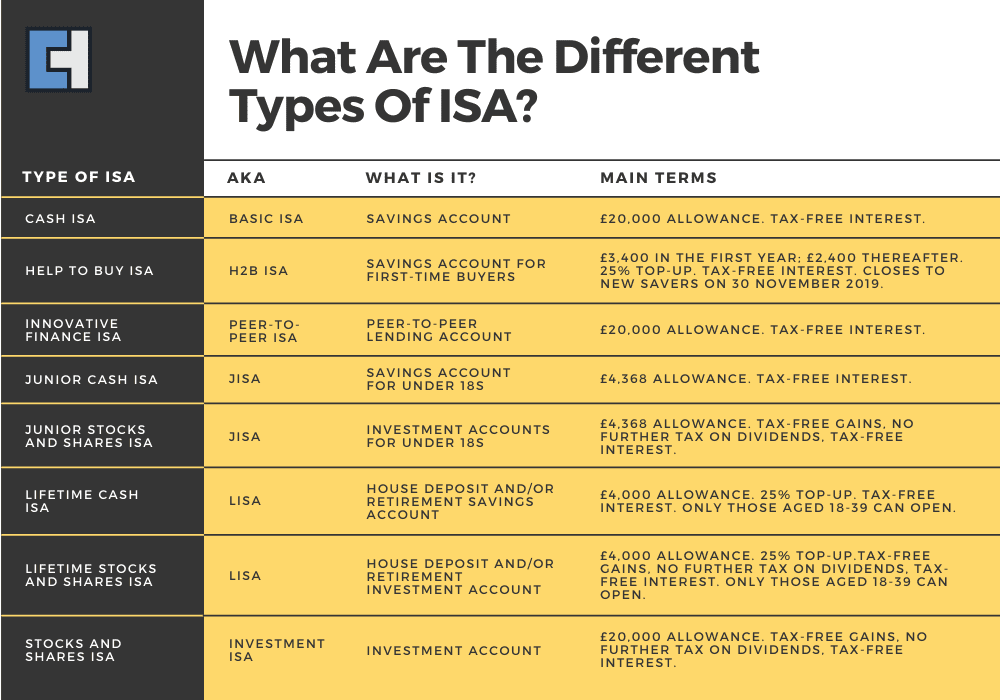
The Different Types of ISA Accounts
Four different Individual Savings Account (ISA) options are accessible to adult individuals.
1- Cash ISAs
2- Stocks and shares ISAs
3- Lifetime ISA
4- Innovative Finance ISA
Parents can establish a Junior ISA on behalf of their children. However, this does not impact their own personal ISA allowance. The Junior ISA is held under the child’s name.
Cash ISAs
Cash ISAs are very similar to regular savings accounts. Picture this: Your money sits there in the report, within your easy reach, depending on the specific conditions of the account. The big bonus? With a cash ISA, your savings interest isn’t taxed.
You’ve got quite a few cash ISAs to pick from, too. They might seem like these all function the same way, but actually, these can vary – think differences in how much interest they pay out or how much advance notice you need to give before making a withdrawal.
Easy Access ISAs
Easy access ISAs represent the most straightforward kind of cash ISA. They are specially designed to give you free access to your money whenever you desire.
Typically, these ISAs permit an unlimited number of deposits and withdrawals with no penalties, although it’s essential to remember that some may have certain restrictions.
In most cases, easy access ISAs come with fluctuating interest rates. It means your initial rate can increase or decrease as time passes.
Fixed-rate ISA
If you have some extra cash you’re confident you won’t need access to anytime soon, you might want to think about investing in a fixed-rate ISA. This type of cash ISA is where your initial deposit is stashed away for a certain period and earns a fixed interest during that time.
This period could be anything from one to five years, with longer terms usually offering higher interest rates.
Note: If you try to withdraw from your fixed rate ISA before the period ends, you could pay an interest penalty, and your ISA might even be closed.
Notice ISA
There’s a variety of cash ISAs out there. One of these is called a notice ISA. This option can provide you with higher interest rates than a standard, easy-access ISA – and it offers you more flexibility to withdraw money than a fixed rate ISA might allow.
However, to take out money, you’ll need to alert the bank ahead of time, with the notice periods generally ranging from 30 to 180 days. If you withdraw without adequate notice, you’ll face a penalty – the scale that often matches the notice period.
Regular Savings ISA
A regular savings ISA might be your best bet if you want to save smaller amounts regularly. This type of ISA offers a better interest rate, provided you commit to making traditional, minimum deposits. Be warned: If you skip a payment or withdraw money prematurely, a penalty will be waiting.
Stocks and Shares ISAs
Even though stocks and share ISA can potentially boost your savings as the stock market grows, it’s crucial to remember that risk is involved. Your investment might lose value.
The advantage is that you won’t have to pay any income or capital gains tax on the growth. With a cash ISA, your money is kept, earning interest based on a fixed rate. However, a stocks and shares ISA, also known as an investment ISA, invests your deposited money into funds, bonds, and shares.
Like cash ISAs, the Financial Services Compensation Scheme (FSCS) typically offers protection up to £85,000 if your stocks and shares ISA provider collapses. However, this protection doesn’t cover any losses incurred from your investment. It’s important to note that this type of ISA is more suitable for individuals who can afford to take risks with their money and have a long-term investment perspective.
Tax-Smart Strategies: Capital Gains and Home Office Deductions Explained
Lifetime ISA
The Lifetime ISA (LISA) operates on the principle of the Government providing a 25% bonus on LISA deposits, limited to a maximum of £1,000 per year. The savings and the Government bonus accrue tax-free interest, which can be compounded monthly, annually, or on the anniversary date.
However, there are specific criteria and limitations associated with opening a LISA. Eligibility requires:
1- You should be between 18 and 40, with the first deposit made before reaching 40.
2- You can make contributions up to £4,000 per year until age 50.
3- After turning 50, the Government bonus ceases, but the savings continue to earn interest.
4- Withdrawals from the LISA are permitted only for purchasing a first home, reaching the age of 60 or above, or being terminally ill with less than a year to live. Any other early withdrawal may result in penalties.
5- When using your LISA to buy your first home, the property value mustn’t exceed £450,000.
If you opt for a Lifetime ISA (LISA) as a retirement savings vehicle, you can withdraw funds from your account at age 60. Utilising the savings according to your needs is permissible, although the LISA is primarily intended to provide financial support during retirement.
While a lump sum withdrawal is an option, you also have the choice to make partial withdrawals to supplement your income. The remaining balance in the account will continue to accrue interest and retain its tax-exempt status.
Innovative Finance ISA
In the realm of peer-to-peer lending (P2P), an Innovative Finance ISA (IFISA) allows individuals to lend their deposited funds to individuals small businesses or invest in crowdfunding projects for a predetermined period.
The aim is to generate tax-free returns on the initial investment after the specified timeframe. It’s important to note, however, that returns are not guaranteed, and there is a level of risk involved with the invested capital.
Unlike a stocks and shares ISA, an IFISA does not protect the FSCS in the event of the provider’s collapse.
How Do You Transfer an ISA?
You can move your ISA savings to a different provider, including another type of ISA, whenever you wish.
If you have money saved from previous tax years, it will not affect your allowance. Any money, no matter how big or small, can be transferred at your discretion. For instance, you can transfer £15,000 from your old cash ISA to a new stocks and shares ISA, and you can still make a further £20,000 contribution in the same tax year.
All contributions made in the current year, including any growth associated with them, must be transferred in full. After the transfer is finished, you will still have some permission. There are a few important things to remember when moving your ISA. First off, taking physical withdrawals of the funds is not recommended. It is advised that you contact your new provider and ask them to manage the transfer on your behalf.
When you switch to a new provider, you may be required to pay an additional fee for the initial set-up or advice. If you possess a Lifetime ISA, it is essential to be aware that transferring to another type of ISA (before your 60th birthday) is considered a withdrawal, resulting in a fee application.
How Do You Open an ISA? | Setting up an ISA
Different banks give you several ways to operate an Individual Savings Account (ISA). You can go to a local branch, send an application by mail, use their online platform or a mobile app, or even call them.
Usually, you’ll need to deposit an initial to open an ISA, which can vary from as little as £1 to thousands of pounds. However, some ISAs might ask that you commit to a minimum regular deposit each month.
The provider of the ISA will also require certain personal information from you, such as your complete name, address, national insurance number, and signature. You must thoroughly read the ISA provider’s declaration and carefully comprehend any limitations or fees associated with withdrawing funds from your ISA.
How many ISAs can you have?
In each tax year, you can establish an investment ISA, a cash ISA, and an innovative finance ISA. Once the new tax year begins in April, you can open one of each category again. Consequently, over several years, you may accumulate many ISAs.
No matter how many ISAs you open, your tax-free ISA allowance is limited to £20,000 per tax year. It’s also important to note that even if you have multiple ISAs of the same type, you can only pay into one each tax year. If you have a few different ISAs, you might choose to pay into the one with the best interest rate.
Can You Move an Individual Savings Account (ISA) to a Different Provider?
Many ISA providers offer the flexibility to transfer your ISA funds from one provider to another. For a variety of reasons, such as to switch to a different provider with a wider range of investment alternatives or to pursue a more competitive interest rate, you may want to think about transferring your individual savings account.
If the interest rate on your current account has dropped dramatically, you should consider shifting your ISA. Even in low-interest rate environments, it is always beneficial to maximise your prospective interest returns.
Your annual ISA allowance shouldn’t be impacted if you move an Individual Savings Account (ISA) correctly. On the other hand, you will use up your ISA allowance if you physically move your ISA by taking all of the money out of one ISA and putting it into another.
Most providers will accommodate this request if you wish to continue using the same provider for your ISA but want to transfer your funds to another ISA product or type.
Can You withdraw from an ISA and deposit the funds Later?
If your Individual Savings Account (ISA) is considered ‘flexible,’ you can withdraw funds and repay them within the same tax year, all without depleting your ISA allowance.
Moreover, you can withdraw funds initially deposited in previous tax years. Should you choose to repay these withdrawn funds before the conclusion of the current tax year, it will not have any impact on your ISA allowance for the present year.
When you attempt to reinvest the money that you take from a non-flexible Individual Savings Account (ISA), it will be counted against your ISA allotment as if it were brand-new money.
Your ISA funds lose their tax-exempt status if you move them to a standard savings account. If this is the case, HMRC will tax the money while taking your personal savings allowance into account, if any.
Conclusion
In summary, without paying income tax on interest or investment returns, Individual Savings Accounts (ISAs) offer incredibly flexible and tax-advantageous methods for people to increase their wealth. They provide several solutions to suit different risks and savings goals.
When deciding what to buy, it’s critical to understand the subtle variations between each type of ISA. Your goals and financial status should guide the decision you make. When selecting the best individual savings account (ISA) for you, don’t forget to take your risk tolerance, investment horizon, and specific savings objectives into account.
About Clear House Accountants
At Clear House Accountants, we redefine the role of conventional accounting corporations, embracing a destiny-ahead method that transcends conventional barriers. As leading accountants in London, we are satisfied with being more than just economic experts; we’re architects of empowering business ecosystems. Our virtual accountancy exercise is fueled by innovation, adaptability, and contemporary technology, ensuring our clients thrive in an ever-evolving commercial enterprise panorama. With a commitment to sparking creativity and fostering increase, we offer comprehensive and scalable offerings, which include Management Accounting, Cost Accounting, Bookkeeping, Statutory Accounting, and Tax, allowing corporations to extract priceless insights and data.
Partner with Clear House Accountants to navigate the complexities of UK accounting and tax laws and elevate your commercial enterprise to new heights.