RTI Penalties
The term RTI stands for Real-Time Information, which aims to improve the Pay As You Earn (PAYE) information submission process. The PAYE is the information regarding employee payroll that employers submit to HM Revenue & Customs (HMRC). The RTI system was designed in the interests of HMRC, employers, and employees. HMRC impose RTI penalties if the legislation is not being followed or if the submission is not made on time or correctly
HMRC as per legislation confirmed that reporting RTI is compulsory for all employers who manage employee pay. This regime has been mandatory for most employers since April 5th 2013, while a few big employers joined in April 2012.
Related: If you have recently started operating as an Employer, you might want to read seven essential payroll tips to get you started correctly.
What is RTI:
Under the RTI regime, employers are required to submit information to HMRC in real-time The new regime does not require the submission of certain old forms anymore like P14, P35, P45, P46, and P46 (pen).
Filing PAYE includes several electronic submissions that employers can make at different intervals. Employers can do that through payroll software or a payroll company. If the filing needs complex solutions, employers may outsource payroll to a competitive Payroll Accountant or Payroll bureau. The filings are:

Required Submissions
A full payment submission (FPS)
FPS is made before or on the time when an employee gets paid. It includes all the details regarding employees, their pay and deductions. Employers are expected to submit an FPS before or on making payment to their employees.
However, if the employer has more information to send after April 5th, they can send it through the FPS by April 19th. After that, they can submit the information on EYU (Earlier Year Update). New employers get 30 days to submit their first FPS.
An earlier year update
An earlier year update is made to correct any errors or to make adjustments to the previously submitted information. The submission of payroll information through EYU follows the end of the tax year.
An employer payment summary
An employer payment summary, EPS is a monthly process to highlight any changes made to the payments to HMRC for SMP and SSP.
Nothing to report regarding returns
HMRC expects submission even if no payments are made in the month. In case of no payment, the submission must be made by the 19th of following the end of the tax month.
Employee forms P60 and P11D
Employers are required to provide a P60 end-of-year summary and P11D to their employees by May 31st and July 6th, respectively, following the end of the tax year.
Payroll Software
Employers can use payroll software that HMRC has provided for a very basic fee for up to ten employees. However, most employers find it convenient to purchase their own RTI-enabled payroll software to generate their returns. Employers in need of a reliable payroll accountant may outsource their payroll to an accountant or accountancy firm.
Tip: Our Payroll health check can help you identify key weaknesses in your payroll function.
Planning point: There are a few HMRC approved payroll software but make sure your software can perform earlier year updates before selecting it.
Video: RTI Penalties
What happens if you do not report payroll information on time? watch the video to get the answer.
As per HMRC, penalties apply if you submit your payments on the FPS after the payment date. Moreover, if you did not send all the FPS or did not send in an EPS, as no employee is paid during the month
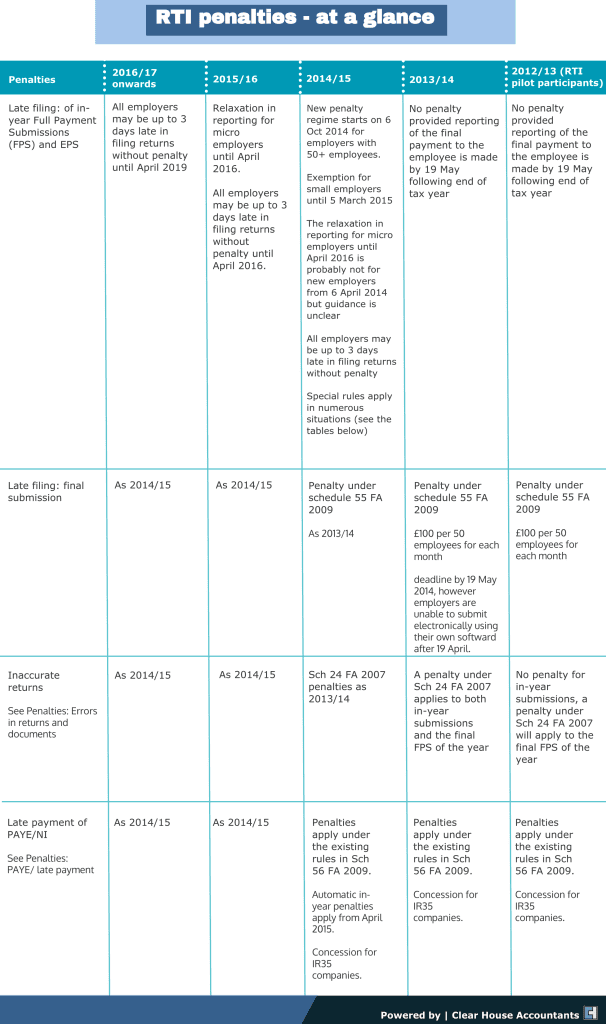
According to Sch 56 FA 2009, penalties apply to all monthly or quarterly PAYE and National Insurance (NI) payments. HMRC introduced automatic in-year penalties in April 2015. The automatic calculation is based on the risk involved and the number of late payments. Following is a detailed insight into the penalties and their application.
- End-of-year penalties
Under the RTI regime, an employer has to make sure that FPS is filed for the final payment of the tax year. In addition, HMRC does not require the submission of a P35 or P14 anymore. The year-end penalties are applicable if the employer fails to report year-end FPS to HMRC. HMRC notifies the employer regarding the penalty by September following the tax year.
- Penalties for inaccurate in-year RTI submissions
According to Sch 24 FA 2007, penalties are applicable for inaccurate in-year RTI submissions for filed returns since 2013/14.

- Late payment of PAYE
According to Sch 56 FA 2009, penalties are applicable for late payment of PAYE penalties, which remain unchanged in RTI reporting.
Personal service companies sending out deemed employment payments under IR35 get special concessions.
- Late submission of in-year returns
Penalties for late submission of in-year returns are applicable from October 6th 2014, for employers with 50 or more employees under a PAYE scheme. Small employers with more than 50 employees will face the consequences from March 6th 2015. In addition, employers with less than ten employees utilising relaxed reporting requirements may face charges after April 6th 2016,
In all cases mentioned above, the first late submission of the year is ignored. However, it is possible only if the employer is not registered with HMRC under an annual scheme.
The condition of late filing applies to FPS and EPS reporting. For instance, there is no payment to report during the accounting period; the employer is still expected to submit an EPA return by the 10th of each month. An employer may avoid the late filing penalty based on a reasonable excuse.
“Tip: Our expert Payroll Service appeals team can help you make an effective claim against a RTI penalty.”
RTI Penalty Rules
- No penalty applicable on three days late payment
Anyone facing a late filing penalty since October 6th, 2014, may appeal if it was three days late or less. This measure was at first only applicable until April 2016 but extended later on to April 2018 in September 2017. In June 2018, the last date of appeal was extended to April 2019.
Employers who regularly file late payments within three days may not avoid penalty on appeal.
- Micro employers may report monthly
In August 2014, HMRC announced the following rules:
A temporary relaxation for micro employers having nine or fewer employees.
Existing employers, until April 5th 2016, may report PAYE information on or before the last payday in the month.
Moreover, this monthly based reporting rule allowed those who run payrolls, to go on a vacation for more than a week.
What are the RTI late filing penalty rates? Commencing on or after April 6th 2014
The monthly penalty for late filing is dependent upon the number of employees
| Monthly penalty (£) | No. of employees |
| 400 | 250+ |
| 300 | 50-249 |
| 200 | 10-49 |
| 100 | 1-9 |
If there is any penalty, it will be due within 30 days of the penalty notice being issued.
Charging Interest
HMRC confirmed that from April 2014, it would be charging interest on payments including penalties which are not paid by the relevant due date. Prior to this HMRC charged interest only for the last month of late payments.
Related: There might be further risks and complications applicable to you if you work within the contracting industry and use your own PSC to operate, read more about how the changes in off-payroll working in the private industry might impact you shortly.
Tax-Trap in disguise
HMRC confirmed its plans to use a risk-based approach regularly to identify non-compliant employers to responsibilities and penalty-liable individuals. It is vital to make sure the application of essential processes to improve payroll to reduce this risk. An identified non-compliant employer of their legal obligations will be subject to late payment penalties.
Under the Sch 56 penalty regime, HMRC will always charge a penalty. However, Employers may get an exception if HMRC and the employer reach a late payment agreement before the due date.
HMRC may send an official notification on priority to any employer who might have defaulted while filing or on a payment obligation. This step is to ensure that they return to compliance rapidly and mitigate the risks for potential penalties for any failure in the future.
HMRC may send a separate penalty notice for each incorrect filing if they find out that the employer has been filing inaccurate in-year returns in a row.
Even though payroll might seem simple, however, if done incorrectly, the process can get complicated and costly very quickly. Therefore, we suggest outsourcing this process to a reliable payroll accountant. Outsourcing will enable the business owner to focus on the core business operations enabling the business to grow faster.
Clear House Accountants are specialist Accountants in London who have been operating payroll for a large number of businesses, implementing smart solutions and effective payroll processes. Speak to us to see how we can outsource your payroll function to give you more time to focus on your business growth.