Business Startup Costs
Startups face numerous challenges, with cash flow being one of the most pressing concerns. This financial strain often prevents new businesses from hiring specialised startup accountants who could help navigate various financial issues and maximise tax reliefs, sometimes even covering the initial cost of hiring that accountant.
Businesses during their infancy incur many sunk costs that cannot be recovered even if the business succeeds; therefore, it must carefully devise a business plan that should enable it to determine the resources required to operate successfully.
Among the many hurdles that startups face, the primary concern for a majority of new businesses is a lack of cash flow; this even stops them from appointing specialist startup accountants, who would be able to sort out many issues and claim a lot of relief , sometimes even enough to cover the initial cost of hiring that accountant. Businesses during their infancy incur a lot of sunk costs that cannot be recovered. Even if the business achieves success, it must therefore carefully devise a business plan which enables it to determine the resources required to operate successfully.

Part of the plan should be to take advantage of the expenses incurred to reduce tax either in the current year or future years, plus claiming all potential reliefs such as R&D Tax Relief, Patent Box Relief, etc. A fair idea of the deductible business costs also adds a significant advantage. For a business to claim tax relief, it must be trading, and the expenses should be set off against the income it generates. However, this is not the case for startups and potential businesses that haven’t started trading yet, for which pre-trading expenses can be used for tax-related deductions.
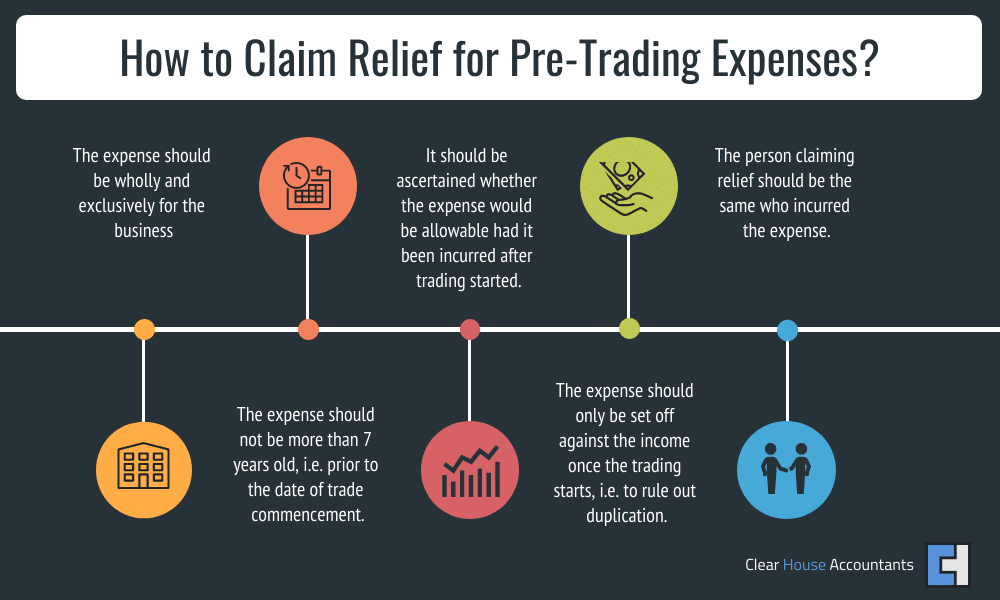
What are the guidelines for claiming these reliefs?
Pre-Trade Expenses
As they say, ‘Ideas are a dime a dozen; it’s the execution that counts.’ Startups that successfully transition from the realm of ideas to the implementation domain face several challenges. The business might need dedicated premises to operate from, such as a warehouse, to store products and other facilities, depending upon its operations.
A whole set of expenses awaits potential entrepreneurs who possess the will but struggle with managing resources. While not initially eligible as organisational costs, these expenses become allowable for tax deductions once the business begins operations.
HMRC’s Guidelines for Pre-trade Expenses
As per the S57 Income Tax (Trading and Other Income) Act 2005 and S61 Corporation Tax Act 2009, pre-trading expenditure is treated as incurred on the day on which the trading starts, i.e. it is included in the profit or loss during the first accounting year. No separate claim for loss relief is required. Further details can be read in HMRC’s manual BIM46351 – Specific deductions.
Pre-Trading Expenses and Their Deduction
Can you claim expenses before a Business Starts in the UK
Example Case study: Let’s suppose that you start a business and have pre-incorporation expenses such as hiring staff and paying suppliers, all valid deductible costs for a business as long as they are wholly and exclusively for business purposes. It is also reasonable for you to draw a salary as part of the startup business costs from the business. HMRC permits the withdrawal of a salary, i.e., at a fair rate according to the extent of work. These costs are adjusted against the business’s income (if any) during its first year of trading.
The rules set out by HMRC allow expenses for up to 7 years before the date when trade commenced to be deductible, which gives businesses plenty of time to deduct these for tax purposes. In some cases, the businesses may take more than usual to take off, such as a construction business, but in that case, exceptions can be made by HMRC to remain fair. If a business is not able to get stable even after seven years, it could be that the business model is not a traditional one and that other options need to be looked at, such as Private Equity or VC Funding. You can review more details about funding using our Funding Guide.
Video: Startup Pre-trade Expenses
Exceptions to Claiming Pre-Trading Expenses
Some expenses cannot be treated as per the rules of pre-trading expenses, such as rentals for a post-trading period or other prepayments. Such payments should be dealt with by the matching concept, i.e. expenses will be set off against the income of the same period in which the obligation arises. The expenses are, however, technically incurred before businesses can start trading, but as they belong to a post-trading period, they already fall within the ambit of tax-deductible expenses. Therefore, there is no need to justify them as pre-trading tax-deductible startup costs.
Start-up Costs for a Business
- Business registration fees
- Legal fees for contracts
- Initial inventory purchase
- Website development costs
- Office rent or lease
- Marketing and advertising expenses
- Employee salaries and wages
- Business insurance premiums
The Cost of Finance
The pre-trading expenses that a business incurs might also include interest payments. A startup can draw loans to finance assets, pay employees, or pay any license fee imminent to trade. The costs of raising this debt finance are termed non-trading debts as they have been incurred before the business can start trading.
According to the loan relationship rules, which govern the pre-trading interest incurred by a company, companies can only use non-trading credit (income), e.g. interest received, to set off the non-trading debit for corporation tax deduction purposes. It might take years for a business to generate non-trade credit income and to claim relief for the pre-trade interest expenses.
Exception to the Rule
If a company cannot generate non-trading credit (income) sooner, then non-trading debits can be elected to claim relief against trading income. The election will alter the nature of non-trading debits to trading expenses, making them deductible startup costs during the first accounting period.
As per the CTA09/S330, the company can elect for non-trading debits if:
- The election has been made by the company within two years from the end of the accounting period in which the debt was taken
- The company commences trade within seven years from the period in which the loan was drawn
- The expense would have been treated as a trading expense had it been incurred in the post-trading period
Conclusion:
It would not be an exaggeration to say that startups act as small economic engines, lifting the country’s overall economy through innovative products and the infusion of new dynamics in the market.
Startups act as conduits of knowledge and ideas, leading to technological breakthroughs; they have a flexible structure that aids the transformation of ideas into products faster than the bureaucratic setups of already existing organisations.
A successful startup might transform the host town or city into a business or a tech hub, like Google has transformed Silicon Valley in California, or just like Infosys has transformed Bangalore in India. Still, the right support is required to create a success story out of a startup.
Cash flow management is the most problematic area for a company that has yet to start its trading but is already incurring expenses. In the UK, the government and the HMRC have laid out specific guidelines for startups to use their pre-trading expenses for tax deductions. These expenses are treated as if they’re incurred on the first day of trading, thus reducing that period’s income and, ultimately, the tax. As a startup, you should not only determine the best sales strategy but also how you will manage and run your business, whether it’s a limited company or another structure.
Additional Resources