A universal consumption tax based on the value added to goods and services is known as value-added tax or VAT, which is imposed in the UK. It applies to almost all goods and services bought and sold for use or consumption in the UK. Therefore, items sold for export or services provided to clients in other countries generally include VAT.
Over the next decades, the VAT regulatory framework in the United Kingdom saw several important changes, one of which was raising the standard VAT rate from 17.5% to 20% in 2011. In advance of the UK’s withdrawal from the EU in January 2021, recent modifications to the VAT reporting requirements have been implemented.
A wide-ranging tax that, in theory, entails all commercial operations, such as the production, advertising, and distribution of products and services. However, if a company’s annual turnover is below a predetermined amount (the threshold), which varies by Member State, they are not obligated to impose VAT on their sales.
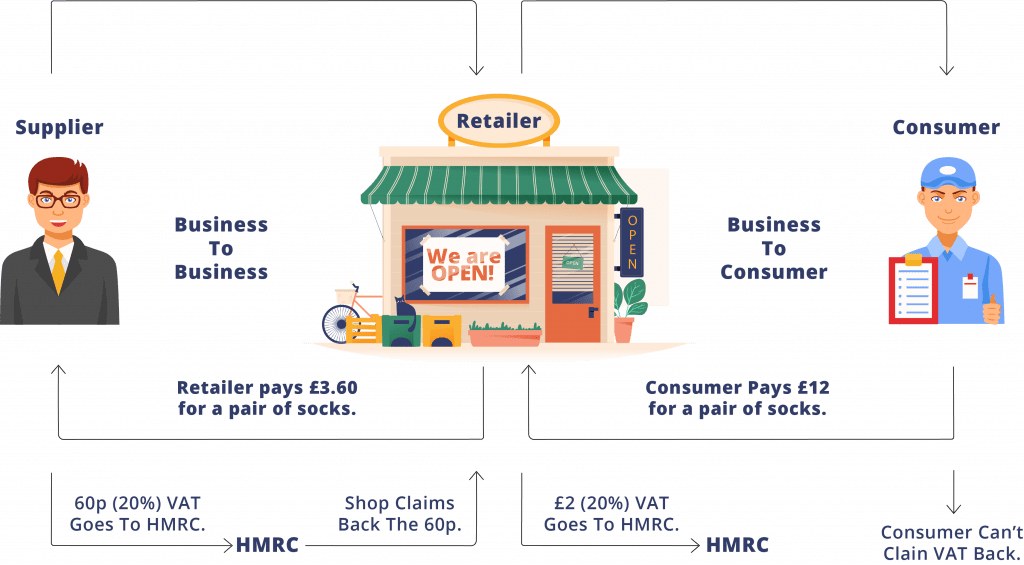
The manufacturer, distributor, and retailer serve as VAT collectors in the supply chain.
Explore the transformative impact of Brexit on VAT for contractors and deepen your understanding of VAT essentials with our thorough guide on VAT returns and compliance.
Key Points About VAT
- A wide-ranging tax that, in theory, entails all commercial operations, such as the production, advertising, and distribution of products and services. However, if a company’s annual turnover is below a predetermined amount (the threshold), which varies by Member State, they are not obligated to impose VAT on their sales.
- It is referred to as a consumption tax since the final consumer is the one who ultimately pays it. Businesses are not charged anything.
- Levied as a percentage of the purchase price suggests that the whole tax burden may be felt over the entire manufacturing and distribution process.
- A partial payment method enables VAT-registered taxable companies to deduct from the VAT they have received the tax they have already paid to other taxable parties on purchases they made for their commercial operations. No matter how many transactions there are, this strategy guarantees that the tax is neutral.
- Although the client rarely pays the seller as part of the purchase price, the “taxable person,” the person who sells the items, is the one who pays the taxation authorities. As a result, it is an indirect tax.
Explore our easy guides to learn about postponed accounting, VAT registration, handling returns, and managing VAT before registration.
How Does VAT Work?
VAT is computed based on the gross margin at each stage of an item’s production, distribution, and sale.
Each level assesses and collects the tax. This approach does not force customers to pay any taxes, unlike a sales tax system, where the consumer is the only one evaluated and responsible for paying the tax at the ultimate end of the supply chain.
For any earlier tax payments made by the taxable person, the fraction of the sale price that represents the VAT owing on a certain transaction may be decreased. This prevents double taxation by only taxing the value added during each step of manufacture and distribution.
Since the ultimate price of the product is equal to the total of the values added at each previous stage, the final VAT paid in this approach consists of the total of the VAT paid at each stage.
What are the VAT Rates?
As per regulations, only the standard VAT rate and the reduced rate are required to be at least 15% and 5%, respectively. (only for delivering the products and services mentioned in a comprehensive list).
Real rates are implemented differently inside the UK depending on various product categories.
There are 3 types of vats
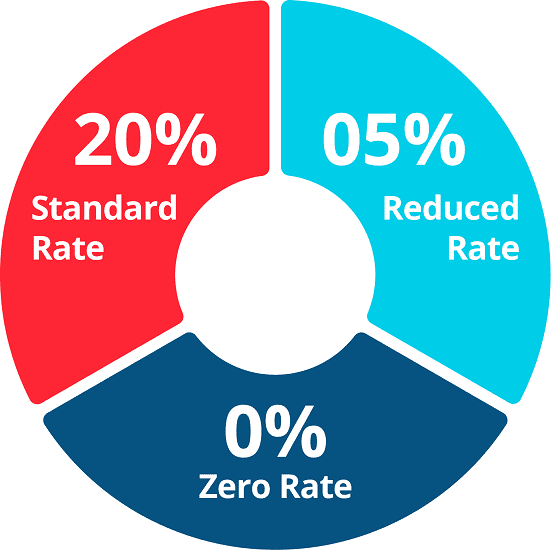
Standard Rate
The standard VAT charge rate in the UK is 20%. Included are the vast majority of products and services. Everything considered a luxury good falls under this category; therefore, meals like ice cream and sweets are taxed at the usual rate. One must have a strong understanding of the standard rate to properly understand how VAT operates for your business.
Reduced Rate
Products that are frequently less expensive are those that are viewed as necessary by the majority of people. Different contribution fees, child safety seats, ecologically friendly practices, and elderly mobility aids are among them. The lowest VAT rate in the nation is 5%. The tourism and hospitality industries are now classified as having lower rates.
Zero Rate
For the final and last VAT categories, the nominal VAT rate is 0%. VAT is not applied to the sale of these goods. Most individuals consider them to be needed. Here are a few things and services that are exempt from UK sales tax.
- Children’s footwear
- Equipment
- magazines, and books
Since rates might fluctuate, you must utilise the most recent ones that are in effect that day.
READ MORE: VAT on Education can get complicated as few services are exempted from VAT, and you might have to pay VAT for others.
Different Types of Value-Added Tax
VAT covers multiple business operations and can be complex to understand at times. Each business operation demands certain considerations be made to ensure accuracy and compliance.
Some of the types are:
- VAT on Land and Property VAT
- Construction VAT
- VAT on Imports and Exports
- International services VAT
- VAT on buying or selling a business
- Explore the nuances and implications of ‘The Impact of the VAT Domestic Reverse Charge‘ on business transactions and VAT reporting.
- Discover ‘All You Need To Know About The Import One-Stop-Shop‘ for streamlined VAT on imports.
VAT Schemes
You can join a VAT scheme if your business is registered for VAT. The following are a few schemes that you might want to take advantage of.
- Flat Rate Scheme
- Annual Scheme
- Capital Good Scheme
- Margin Scheme
- Retail Scheme
Why Should You Register for VAT?
You should register in order to be eligible for a VAT refund on any purchases made; businesses that are registered for VAT must include VAT in their sales invoices. Even if you are not registered for VAT, you are still required to pay the VAT on your purchases since you cannot make a claim for it.
- If You earned more than the VAT threshold that is £85,000 in VAT-taxable income during the course of the last 12 months. (The VAT ceiling) then you should register
- Within the next 30 days, you expect sales to reach £85,000.
- If any of the following apply, you must register regardless of your VAT-taxable sales.
- You give the UK any products or services (or expect to in the next 30 days)
How to Register For VAT?
There are two ways to register for VAT: one is through an agent, and the other is online.
Through an Agent.
You can have an accountant do your VAT Returns and speak on your behalf when contacting HMRC (or an agent). Even if you’re working with an agent, you may register for a VAT online account after you have your VAT number and select the “VAT submit returns” option.
Online
Another way is to register online. You may register for VAT by opening a VAT online account, often known as a “Government Gateway account.” To submit your VAT Returns to HM Revenue and Customs
One important aspect to consider here is that VAT registration obligations vary from case to case. For example, community pharmacies can have different obligations. Similarly, the scenario becomes different for Used Cars, Food Businesses, Entertainment Industry, and so on.
What if You Don’t Register for VAT
If you don’t register for VAT or cannot understand VAT complexities, HMRC could penalize you severely, damaging your reputation.
Services that Fall Under the Purview of VAT
You must first have a thorough grasp of the great majority of goods and services subject to VAT to comprehend how it operates fully. The following goods and services are chargeable with VAT:
- Financial transactions
- Loaned objects
- Selling corporate property
- Gift-giving and bartering for “non-sales”
- Commission
Services that are Exempted from VAT
Some of the services VAT is not allied with are Charities that raise funds through financial, insurance, and credit-related operations for training and education membership fees for organisations. This exemption does not apply to purchasing, leasing, or renting commercial real estate or buildings.
Conclusion
Value-added tax (VAT), often known as a consumption tax, is levied on the value added at each stage of creating goods or services. Each business in the value chain receives a tax credit for the VAT that was previously paid. It is a tax on consumption because the ultimate consumer does not pay it.
The VAT was principally developed to eliminate the double taxation and cascade consequences that were frequent under the old sales tax system. The consumer buys the product from the primary stage to the final product through value-added tax (VAT).
Additional Resources
Frequently Asked Questions About VAT
What is the current VAT rate in 2022?
The current VAT rate is 20% for the standard rate, 5% for a reduced rate, and 0% for Zero Rat VAT.
Is VAT always 20% UK?
Yes, most goods and services in the UK are charged at the standard rate of 20%. You are expected to charge the rate unless stated otherwise.
What does the 12.5 VAT rate apply to?
Hospitality Industry. The 12.5 VAT rate applies to the hospitality industry, hotel and holiday accommodation, and certain transactions.