Self-employment in the UK is an empowering way to take control of your career, giving you the creative freedom to work for yourself and make decisions that shape your financial future and enhance your earning potential. Self-employment, regardless of your position—freelancer, small business owner, contractor—means you are in charge. You choose your working schedule, which trading goods or services you provide, and how best to handle your income.
Self-employment is becoming increasingly common in the UK as many people choose to forego conventional work in favour of flexible hours, independence, and the possibility of running a business reflecting their interests. Still, along with this freedom comes the obligation and quest to have the right skills for self-employment. Self-employed people have to keep accurate financial records, pay their own taxes, and follow different legal rules.
- Start self-employment journey by following our guide 12 Easy Steps to Start a Business in the UK.
- Discover Top Home-Based Business Ideas that You Can Start that offer flexible work options to you.
- Kickstart your journey with 9 Simple Business Ideas You Can Start Immediately!
- Learn from Top 5 Business Trends with Rapid Growth to stay ahead in the market.
- Understand the essentials on UK Tax: A Brief Overview of Taxation in the United Kingdom.
What is the Meaning of Self-Employed?
HMRC defines self-employment as running your own business and bearing responsibility for its success or demise. Should you be self-employed, your rights as an employee—including sick or holiday pay—will be absent. You can, however, set your own rates, choose a variety of work, work for several clients, and enjoy running a business on your terms. In order to be considered self-employed in the UK, you must register with HMRC, make regular income declarations, and pay income tax and National Insurance contributions commensurate with your income.
Though it comes with financial difficulties, being self-employed can be immensely satisfying. The main pain points of being self-employed include having an erratic cash flow, tax payment management, and juggling job with personal obligations. The secret is keeping accurate records of all income and expenses, having a separate business bank account, and making plans ahead.
Contractors, for example, frequently struggle with misinterpretation of IR35 rules and the workings of employment intermediary rules, failing to claim allowed expenses, or insufficient tax planning. Learn pertinent tax laws, keep a thorough record of your income and expenses, and see an accountant to make sure you’re on target and avoid the common mistakes contractors make.
- Understand your tax responsibilities as a self-employed individual with How Much Income Tax and National Insurance to Pay?
- Address common challenges with Pain Points for Self-Employed Individuals.
- IR35 rules Basic mistakes made by contractors and how to avoid them?
- Understand the essentials with our Employment Intermediary Rules | Complete Guide.
- Simplify your tax filing process with our Comprehensive Guide to Self-Assessment.
- Manage your finances better with our guide to Best Business Bank Accounts.
Types of Self-employment
Selecting the right business structure is the first important choice you will make on your path to self-employment. Everything from your legal obligations to your taxes will change depending on this decision. Let’s look at several choices to assist in your proper fit.
Sole Trader
Sole traders are the simplest and most often used arrangement for self-employed people in the UK. Running your business as an individual and keeping all the profits after tax, sole traders bear all the liability for any business loss. It’s perfect for freelancers, contractors, and small business owners who are just getting started. Sole traders will sometimes have employees working for them, either freelancers or employees. The main advantages of being a sole trader are simplicity of setup and total control over the business.
As a sole trader, though, your business and you are one and the same. Thus, you are personally liable for any debts or legal problems, and the taxes are charged under personal income tax regulations. You should consult with an accountant for sole traders if you are unsure about where to begin.
Partnership
Although it involves two or more people working together, a partnership resembles sole trading. If you wish to mix knowledge and resources with someone else, this is a great choice. Though the liabilities are shared as well, the profits are equal. Every partner in a general partnership shares equal responsibility for business debts.
Limited Company
Separate from its owners, a limited company offers more defence against personal liability. This means that should something go wrong, your personal assets are usually safeguarded; nevertheless, the arrangement is more complicated, and you have extra legal responsibilities. Forming a limited company could be a better choice if you intend to add investors to your company or want to minimise risk to the company and what has been added to it.
- Get a clear understanding of how limited companies work by using our What is a Limited Company? A Comprehensive Guide.
- Does IR35 apply to Limited Companies? The Ultimate Guide
- How to Start a Limited Liability Company?
Partnerships with limited liability (LLP)
Combining aspects of limited companies and partnerships, a limited liability partnership is a hybrid arrangement. Professionals like lawyers or accountants frequently use it since the partners have limited liability thus they are not personally liable for the business’s debts outside of their investment. Learn more on how to start and run a limited liability partnership.
- Explore further details in How to Start and Run a Limited Liability Partnership? to understand this hybrid business model.
Limited Partnerships
This arrangement calls for at least one general partner with unlimited liability and one or more limited partners who make business investments but have limited liability based on their investment. Though less common, it can be advantageous for particular sectors or for investment needs.
How To Register as Self-Employed In The UK?
Registering with HMRC comes next once you have selected your business structure. You must register as self-employed by October five, following the end of the tax year in which you launched your business. Visiting the HMRC website and completing the online registration form is the easy way to go. You will need simple information, including your business details and National Insurance number. You will use your Unique Taxpayer Reference (UTR) number once registered when submitting your tax returns.
- Start your self-employment journey with How to Register as Self Employed in the UK: The Complete Guide.
UTR Number: Why It Matters and What It Is
HMRC uses your 10-digit UTR number—a code only yours—to identify you as a self-employed taxpayer. Managing your business taxes and completing your annual Self-Assessment tax return depends on this figure. As you will need it every time you contact HMRC regarding your tax affairs, keep it safe and easily available.
Learn How to Register for Self-Employment and Obtain Your UTR
Taxes on Self-Employed: How to Pay Tax When Self-Employed
Being self-employed means you have to report and pay taxes on the income your business generates.
Although your business structure will determine the type of tax returns you need to file and the tax you pay partially, other factors, including your turnover, who you deal with, and whether you have employees.
The table below briefly lists the several taxes that might impact your business and some deductions you might find in your tax computation.
| Type of tax | Details |
| Self-Employed Income Tax | Self-employed individuals are responsible for paying income tax on their earnings after deducting the relevant allowable expenses. |
| National Insurance Contributions | Those who work for themselves pay National Insurance Contributions based on their personal income. |
| VAT—value-added tax | Only if your taxable turnover reaches the registration threshold in any one 12-month period will you be registering your business for VAT. The kind of structure you apply has no bearing on your need or ability to register; any business can do so. You might also decide to register for VAT on your own initiative voluntarily. |
| Loan Repayments for Students | If you have taken out a student loan you may be required to make student loan repayments. |
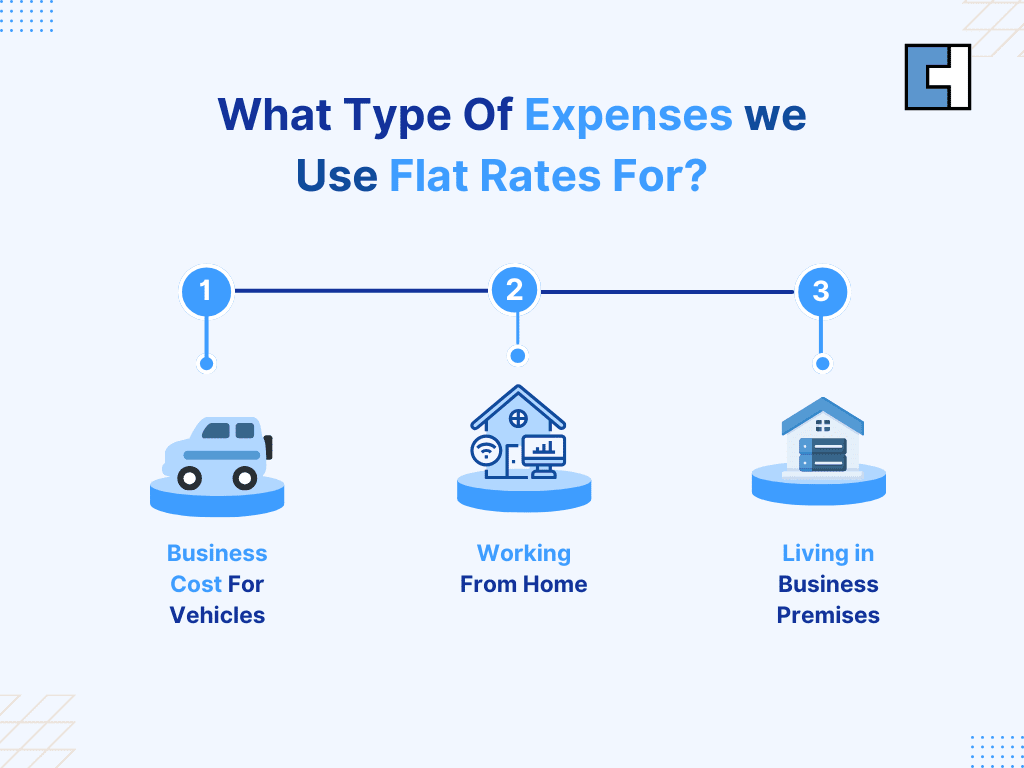
Though the UK tax system is rather complicated, the simplified expenses scheme helps self-employed people to simplify their lives. This lets you figure out some expenses using flat rates instead of computing the actual expenses. For business mileage, working from home, or using part of your house for business use, you could claim simplified expenses. It’s a great approach to cut your documentation and guarantee you’re not losing out on worthwhile deductions.
- Gain a clearer understanding of your obligations with our detailed explanation on How Much Income Tax and National Insurance to Pay.
- It’s crucial to know the consequences; find out What Happens If You Don’t Register for VAT.
- For a comprehensive breakdown of VAT responsibilities, see our VAT Guide for Businesses in the UK.
- For better understanding of the UK’s tax regulations that could impact your business: A Brief Overview of Taxation in the United Kingdom.
- How to streamline your accounting with Simplified Expenses for the Self-Employed Individuals.
- Understand what you can claim with our guide on Claimable Home Office Expenses from Limited Companies.
Tax for Independent Contractors in Trades
Running their businesses can be very expensive for tradespeople, including plumbers, electricians, and builders. Luckily, HMRC lets them apply tax relief on tools, supplies, and travel expenses as well as other costs. Tradespeople can lower their tax load by maintaining careful records and maximising allowed expenses.
Tax Paid by Self-Employed Personal Trainers
Self-employed personal trainers and fitness pros must consider their income from classes, clients, and other services. Often claimed to lower their tax load are expenses including gym equipment, travel, and even continuing education classes.
- To further understand the specific tax considerations for fitness professionals, explore our guide on How do Personal Trainers Pay Tax as Self-Employed Individuals in the UK.
Taxes for Self-Employed Carers
If self-employed carers provide care in their own homes, they could be qualified for particular tax deductions, including those for travel between clients, uniforms, and even some living expenses. Maintaining accurate records of your work-related expenses will help you guarantee your compliance and maximise tax relief.
- Key strategies for maximizing deductions in our Comprehensive Guide: How to Pay Taxes as a Self-Employed Carer
Income From Overseas And The Remittance Basis
If you are a UK resident yet receive income from abroad, you could be liable for taxes. A tax treatment known as remittance basis lets you postpone paying UK tax on your foreign income until it reaches the UK. For those making income overseas, this can be a useful tax plan, but it depends on careful planning to guarantee HMRC rule compliance.
Self-Employed Tax-Free Allowances
Should you be self-employed and work away from home, you might be able to write a business expense for a food allowance. Meals can be claimed as a reasonable cost, for example, if you are on business or client travel, so lowering your tax load.
How Should Your Income from Hobbies be Taxed?
Should your hobby be selling handcrafted goods or providing photographic services, you might have to pay taxes on the money you make from your hobby. Should your income in a tax year be more than £1,000, you will have to register as self-employed and notify HMRC of this income. Claiming hobby-related expenses helps you keep more of your profits and lower your tax-due
What Are The Self-Employment Disadvantages And Advantages
| Disadvantages of Self-Employment | Benefits of Being Self-Employed |
| 1. Unpredictable Income: Income can vary from month to month, especially when starting out, leading to potential financial instability. | 1. Flexibility: You have control over your working hours, allowing for a better work-life balance and the ability to adjust your schedule as needed. |
| 2. Lack of Employee Benefits: Self-employed individuals don’t receive traditional benefits in kind like sick pay, holiday pay, or employer-provided pensions. | 2. Independence: You are your own boss, making decisions about how to run your business, the clients you work with, and the direction you take. |
| 3. Responsibility for Taxes: You are solely responsible for managing your taxes, including filing, record-keeping, and paying income tax and National Insurance contributions. Understand the basics of income tax and NI Contributions | 3. Unlimited Earnings Potential: There is no salary cap, and your income can grow as your business becomes more successful. |
| 4. No Job Security and unpredictable finances: There’s no guaranteed paycheck or job stability, making it risky if your business doesn’t perform well or experiences slow periods. | 4. Personal Satisfaction: Running your own business and pursuing something you are passionate about can be more fulfilling than traditional employment. |
| 5. Administrative Burden: You must handle everything yourself, from accounting to marketing, which can be time-consuming and overwhelming. | 5. Tax Deductions: Self-employed individuals can claim various business-related expenses to reduce their taxable income, lowering their overall tax burden. |
- Adjusting your taxes for hobby income, check out How To Adjust Tax on Income From Your Hobbies.
- Understand the implications of non-cash benefits with our detailed guide, Benefits in Kind Taxation: A Comprehensive Guide
- Understand essential financial obligations with our guide on Income Tax and National Insurance (NI) Basics.
Conclusion
Though it provides amazing freedom, self-employment calls for discipline, planning, and knowledge of financial responsibilities. Working for yourself will pay off if you choose the correct business structure, keep on top of your taxes, and avoid common mistakes. You should always try and remain compliant with HMRC.
As a self-employed professional, handling your taxes, money, and documentation can be taxing. Our team of accountants for self-employed individuals can be of great assistance when looking to remain compliant and save taxes.
Additional Resources
Mostly Asked Questions on UK Self-Employment
What are the advantages of self-employment in the UK?
Self-employment provides independence, flexibility, and the possibility for limitless income. You direct your business operations and working hours. You also can claim tax-deductible costs, which lower your taxable income. Self-employment lets you follow your interests and create a business on your own terms, fostering personal satisfaction.
How do I become self-employed?
Becoming self-employed in the UK is easy. Visit the HMRC website and finish the online Self-assessment registration form to register as self-employed. You will have to supply personal information, including your National Insurance number. Your Self-assessment tax return uses the Unique Taxpayer Reference (UTR) number you obtained once registered.
What expenses can I claim as a self-employed individual?
As a self-employed individual, you can claim business-related expenses such as office supplies, travel, tools, marketing, and professional fees. If you work from home, you can also claim a share of household expenses, including utilities. Maximising deductions and lowering your tax bill depends on accurate record-keeping.
How do I calculate my tax as a self-employed person?
To calculate your tax as a self-employed person, subtract allowed expenses from your total income to find your taxable income. Profits over £12,570 are liable for income tax, with rates ranging from 20% to 45% depending on your income. Your profits also determine your Class 2 and Class 4 National Insurance Contributions. Hiring an accountant or using accounting software can help streamline the process.
Do I need an accountant if I’m self-employed?
Although not required, hiring an accountant can save time, ensure compliance, and help lower your tax burden by claiming all possible deductions. Accountants can also offer financial advice and assist in managing complicated business finances, including your tax return.
How do I handle overseas income?
You must report overseas income on your Self-assessment tax return. Double taxation agreements prevent the UK from taxing the same income twice. If you are non-domiciled, you may be eligible for the remittance basis, postponing UK tax on foreign income until it is brought into the UK. Seeking expert advice can help ensure compliance.